Change can be daunting, even when switching from a lead-acid battery to a lithium iron phosphate battery (LiFePO4). Properly charging your battery is critical and directly impacts the performance and life of the battery. There are many factors to keep in mind when charging a RELiON LiFePO4 battery such as how to charge, the type of charger, which charging profile, how long it takes to charge, and more. Properly charging your battery directly impacts its performance and life. Make sure your battery achieves its maximum life, by, following these simple charging guidelines.
Charging Conditions
Much like your cell phone, you can charge your lithium iron phosphate batteries whenever you want. If you let them drain completely, you won’t be able to use them until they get some charge. Unlike lead-acid batteries, lithium iron phosphate batteries do not get damaged if they are left in a partial state of charge, so you don’t have to stress about getting them charged immediately after use. They also don’t have a memory effect, so you don’t have to drain them completely before charging.
All RELiON LiFePO4 batteries come with a BMS, to protect the battery from over-temperature. If the BMS disconnects due to high temperature, wait until the temperature reduces before using or charging the battery again. Please refer to your specific battery’s Data Sheet for the BMS high-temperature cut-off and reconnect values. Lithium batteries shouldn’t be charged at their normal rate when below freezing. RELiON LiFePO4 batteries can safely charge at temperatures between -4°F – 131°F (0°C – 55°C) - however, we recommend charging in temperatures above 32°F (0°C). If you’re using your battery in sub-freezing temperatures, check out RELiON’s LT Series of batteries.
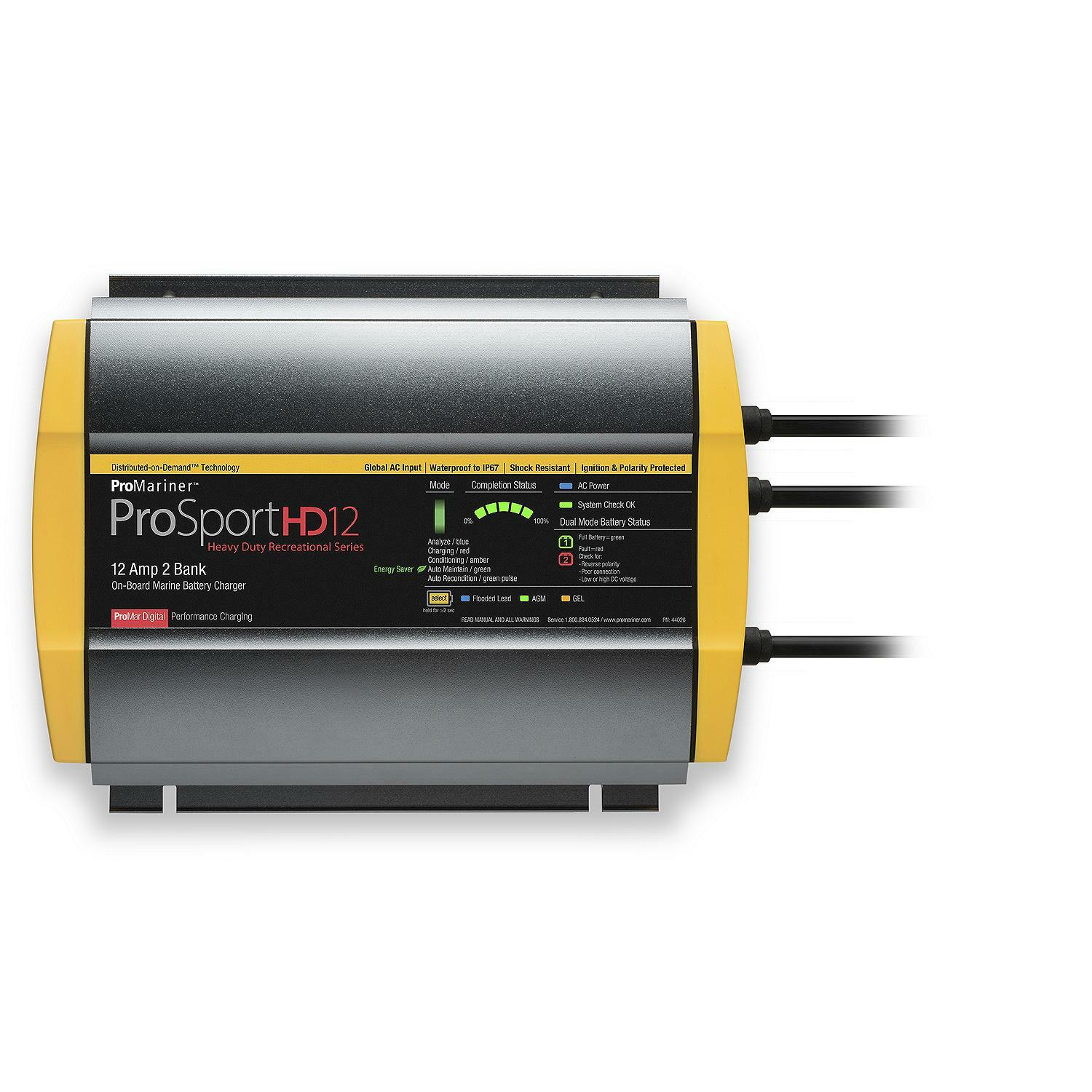

What Type Of Battery Charger Should You Use?
The ideal charger will have a lithium specific setting, like the ProMariner® ProSport HD, and it’ll be programmed with the appropriate voltage limits. Wet lead-acid battery chargers tend to have a higher voltage limit, which may cause the battery management system to go into protection mode and may cause fault codes on the charger display.
Charging Batteries in Parallel Best Practices
Batteries are connected in parallel or in a series. When connecting in parallel, it’s best to charge each battery individually before making the parallel connections. If you have a voltmeter, check the voltage a couple of hours after the charge is complete and make sure they’re within fifty millivolts of each other before paralleling them. This will minimize the chance of imbalance between the batteries and maximize the system's performance. Over time, if you notice the capacity of your battery bank has decreased, disconnect the parallel connections, charge each battery individually, then reconnect.
Charging Batteries in Series Best Practices
Connecting lithium batteries in series is much like connecting them in parallel, it’s best to charge each battery individually and check the voltage to ensure they’re within fifty millivolts of each other before making the series connections.
It’s highly recommended to charge lithium batteries in series with a multi-bank charger. This means, each battery is charged at the same time but completely independent of the other. In some applications, this isn’t practical, which is why RELiON offers 24V and 48V batteries to reduce the need for multiple batteries in series.
Charging Your Batteries While In Storage
Lithium iron phosphate batteries are much easier to store than lead-acid batteries. There’s no maintenance needed on short-term storage of three to six months. Ideally, leave batteries at around fifty percent state of charge before storing. For the long term, it's best to store them at a fifty percent state of charge and then cycle them by discharging them, recharging them, and then partially discharging them to approximately fifty percent, every six to twelve months
Lead-Acid vs. Lithium Battery Charging Differences
Lithium batteries charge at a much higher current and they charge more efficiently than lead-acid, which means they charge faster. Lithium batteries don’t need to be charged if they’re partially discharged. Lead-acid batteries, when left in a partial state of charge will sulfate, drastically reducing performance and life.
The BMS protects lithium batteries from being over-charged. However, lead-acid batteries can be over-charged, which increases the rate of grid corrosion and shortens battery life.

Charging Parameters
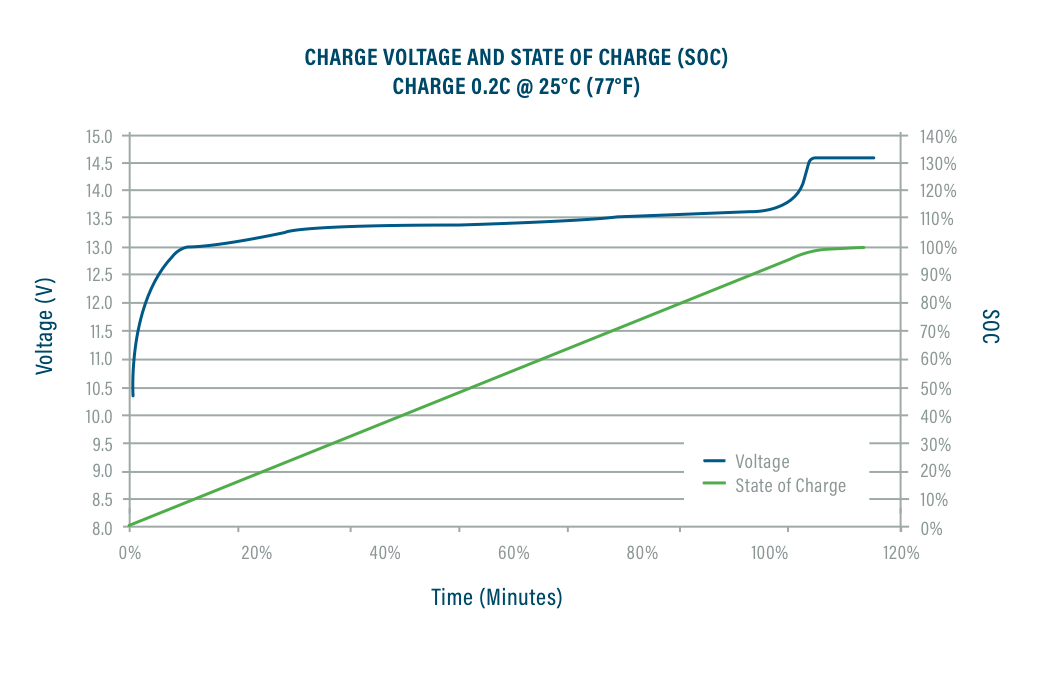
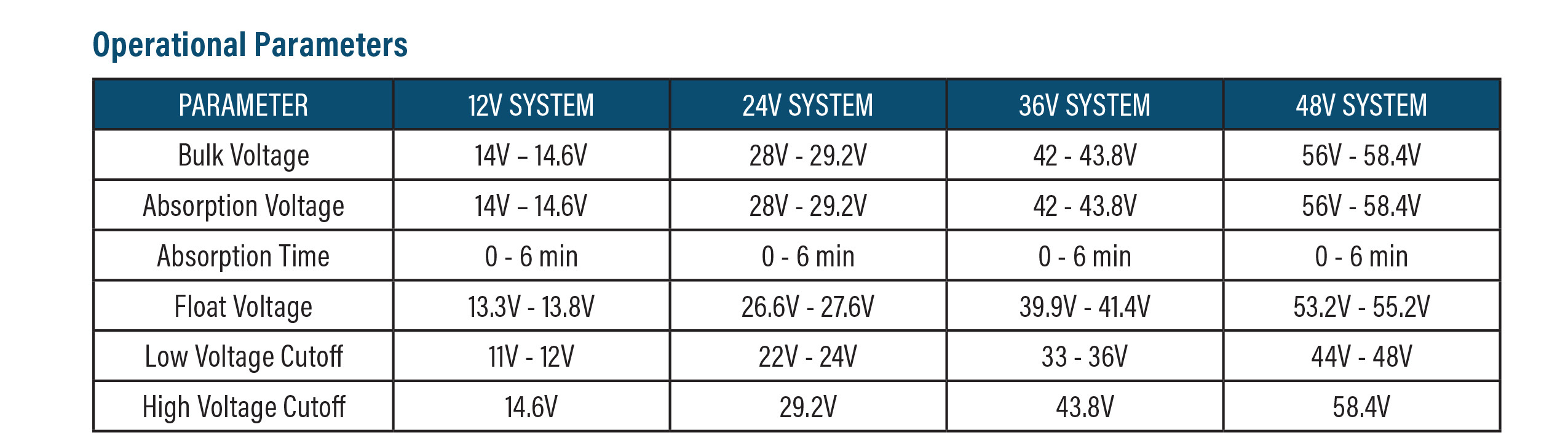
Finally, when using an Inverter/Charger or charge controller, there are parameters you must follow, which are based on the size of the system. For a 12V system, the absorption voltage is between 14 and 14.6 volts with a low voltage cutoff between 11 and 12 volts. For a 24V system, the absorption voltage is between 28 and 29.2 volts with a low voltage cutoff between 22 and 24 volts. For a 36V system, the absorption voltage is between 42 and 43.8 volts with a low voltage cutoff between 33 and 36 volts. For a 48V system, the absorption voltage is between 56 and 58.4 volts with a low voltage cutoff between 44 and 48 volts.
High-quality alternators and DC-to-DC chargers can also safely and effectively charge your batteries. Just make sure they’re compatible with lithium iron phosphate batteries. For the accurate state of charge, you should be using a fuel gauge that measures current, rather than voltage.
For more details on charging your RELiON lithium batteries, check out our charging instructions and contact us if you have any questions.